Medium Clouds
Altocumulus, altostratus and nimbostratus are medium clouds, with cloud base located between around 2,000 to 6,000 metres above the ground. Medium clouds at lower levels are mainly composed of water droplets, whereas at upper levels they are composed of super-cooled water droplets and ice crystals. In the tropics, the top of medium clouds can reach as high as 8,000 metres.

Altocumulus appears as a white, grey, or both white and grey cloud block or cloud layer. It usually has shading in some parts and is composed of laminae, rounded masses or rolls. It sometimes looks fibrous or dispersing. Most of the regularly arranged small cloud blocks have an apparent width of between 1 and 5 degrees*.
This genus can be easily confused with cirrocumulus and stratocumulus. Altocumulus sometimes produces descending trails of fibrous appearance (virga). Coronae and irisation are often observed in thinner parts of the cloud.
According to the “International Cloud Atlas” published by the WMO, altocumulus contains the following types:
Species: stratiformis, lenticularis, castellanus, floccus;
Varieties: undulatus, radiatus, lacunosus, duplicatus, translucidus, perlucidus, opacus;
Supplementary features and accessory clouds: mamma, virga.
* If a centimetre rule is held at arm’s length, a finger span of one centimetre is approximated to a visual width of 1 degree.
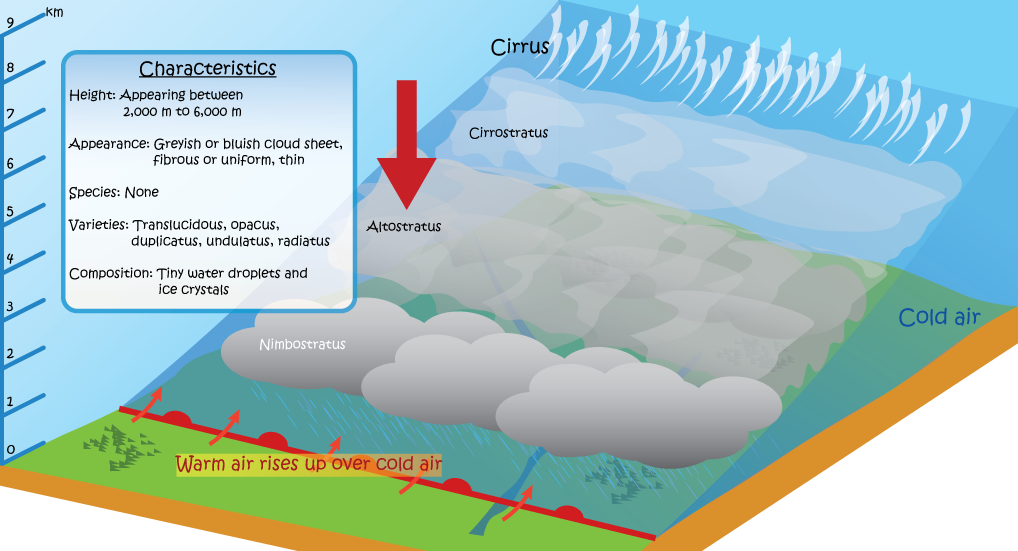
Altostratus is greyish or bluish, in the form of a sheet or a striated, fibrous or uniform layer, totally or partly covering the sky, and having parts thin enough to reveal the Sun vaguely, as if viewing through a piece of ground glass. Altostratus does not show halo phenomena.
Altostratus does not cast shadow of objects on the ground. If the apparent shape of the Sun or Moon can be seen, it should be altostratus rather than nimbostratus. Altostratus has a less uniform base. Uneven thickness of thick altostratus may cause difference in brightness over the cloud layer. At night, if it is uncertain whether the cloud is altostratus or nimbostratus, by convention, it can be regarded as altostratus if there is no rain or snow.
According to the “International Cloud Atlas” published by the WMO, altostratus contains the following types:
Species: None;
Varieties: translucidous, opacus, duplicatus, undulates, radiatus;
Supplementary features and accessory clouds: mamma, virga, praecipitatio, pannus.
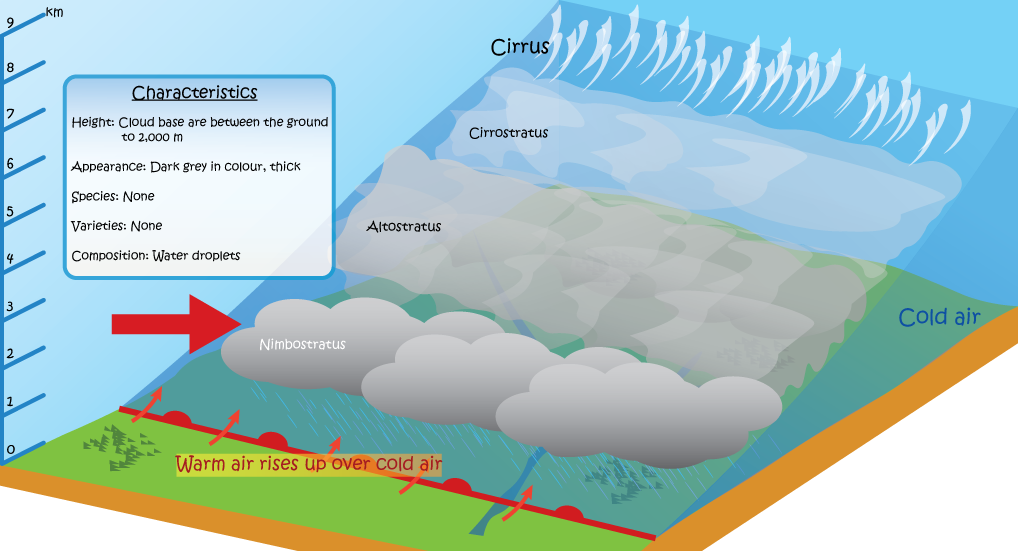
Nimbostratus, a grey and dark cloud layer, often brings continuously falling rain or snow, and blocks out the Sun. Low ragged clouds frequently occur at the bottom of nimbostratus.
Nimbostratus generally forms from thickening altostratus or when a well-developed cumulonimbus thickens and spreads out. Nimbostratus is a thick dense cloud which can be distinguished from stratus by the precipitation it produces.
According to the “International Cloud Atlas” published by the WMO, nimbostratus contains the following types:
Species: None;
Varieties: None;
Supplementary features and accessory clouds: virga, praecipitatio, pannus.