UV Index on
(Hong Kong Time)
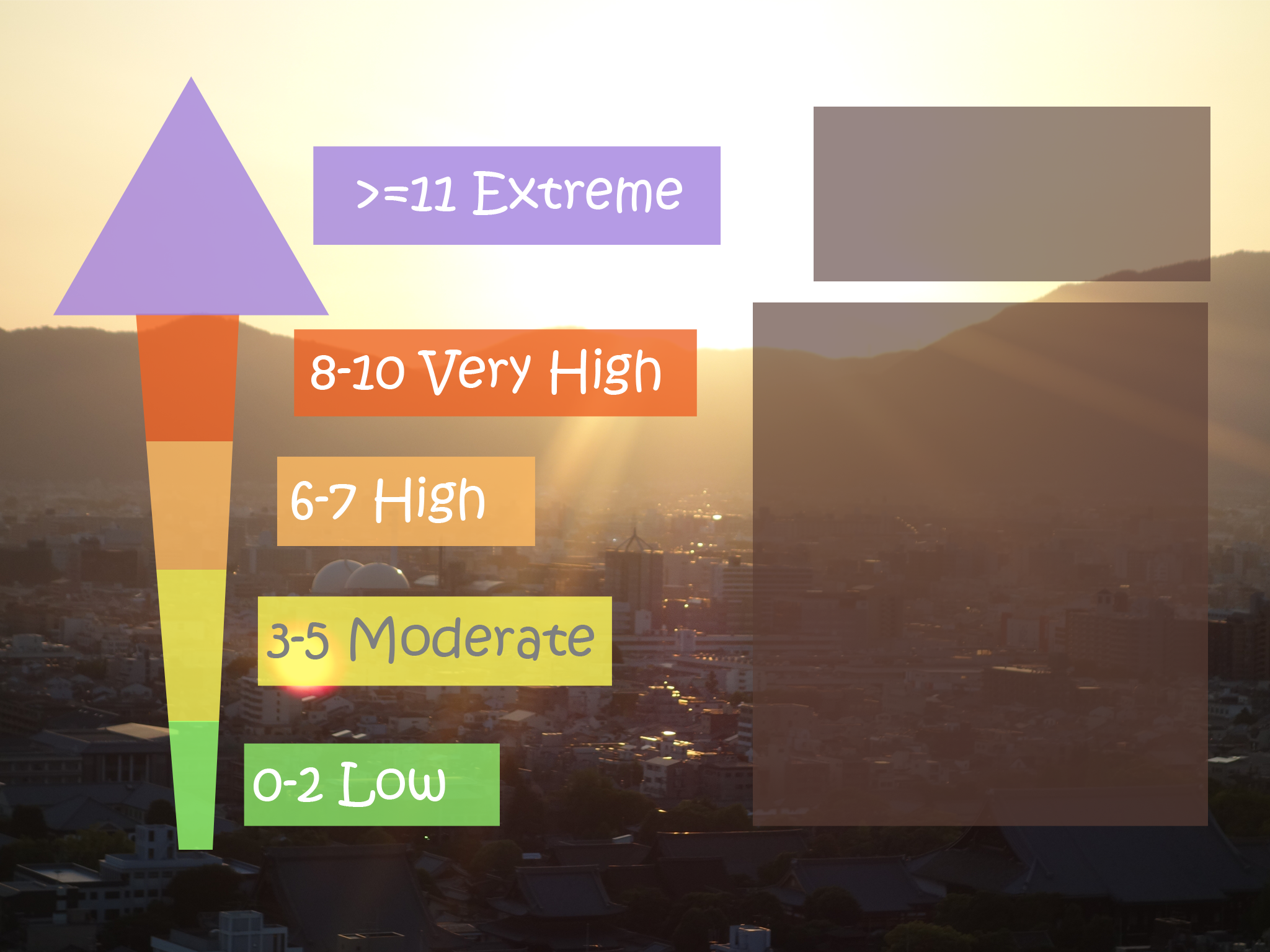
UV Index
|
UV Index
|
Exposure
Level
|
|
0-2
|
Low
|
|
3-5
|
Moderate
|
|
6-7
|
High
|
|
8-10
|
Very High
|
|
>= 11
|
Extreme
|