Weather Photos
-
Weather Phenomena
Extreme Weather
-
Tropical Cyclones
A view from space allows a full appreciation of the majestic nature of tropical cyclones. A closer look can bring out further details. The bright patch near the storm centre is the cirrus canopy - high clouds emanating outwards from the top of the centre. Away from this cirrus shield, some low-level spiral cloud lines can also be seen clearly. Most of the heavy rain occurs near the storm centre and along these spiral rainbands. The rainbands rotate in the same sense as the storm circulation and tend to sweep through an area one after another. At a given location, heavy precipitation is usually pulsing at intervals of a few hours. Squalls and gusts increase during the approach and passage of rainbands. Rain becomes persistent and winds violent as the centre of the storm draws near.
A tropical cyclone is akin to a travelling heat engine. It feeds on an incessant supply of latent heat released from condensation in ascending moist air. The mechanical power generated is in the order of 20 million megawatts and the energy so generated in one day is equivalent to about 20 years' supply of electricity for Hong Kong (at the rate consumed in 1990). The reliance on readily available moisture also explains why tropical cyclones can only survive over the warm oceans and invariably weaken once over land.
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC.
-
Thunderstorms
Thunderstorms are formed by the uplift of warm and humid air. There are many factors that lead to the uplift of air, e.g. solar heating, in the vicinity of low pressure troughs, when two different air streams meet, or when air is forced uphill.
When humid air is lifted, it will be cooled and the moisture in the air will condense to form clouds. Upon further ascent, the cloud will extend higher and the water droplets in the cloud will continue to grow in size. As the cloud extends further upward, ice crystals may form because of the low temperature there. A cumulonimbus cloud results when it grows to a height of 10 to 20 kilometres, and thunderstorms are produced by cumulonimbus clouds.
Photo taken by Jacky Cheng
-
A tornado is a violently-rotating column of air that extends from a cloud down to the ground, and a tornado over water is called a waterspout. In Hong Kong, their occurrences are mostly associated with unstable weather during the rain season from May to September.
Both tornadoes and waterspouts are intense columnar vortices in the shape of funnel clouds with very strong winds and very low pressure near the centre. During their passage, the direct impact of very strong winds and the difference in pressure between inside and outside can shatter buildings with weak structures, and even blow trees and vehicles away. There have been reports of small boats capsizing in nearby waters on encountering waterspouts, while tornadoes or waterspouts reaching the coast have caused damage to buildings in Hong Kong though these do not happen too frequently.
Tornadoes
Photo Library, NOAA Central Library; OAR/ERL/National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL)
-

Crepuscular Rays
The alternating bright and dark strips are caused by shadows of mature cumulonimbus clouds.

Cumulonimbus Cloud
Cumulonimbus clouds are characterized by strong vertical motion of very moist air, developing to a great height. Thunderstorms are usually associated with this particular type of cloud which can extend from near the ground up to 10 kilometres.

Double rainbow
A secondary rainbow is produced when there are two reflections inside a water droplet.
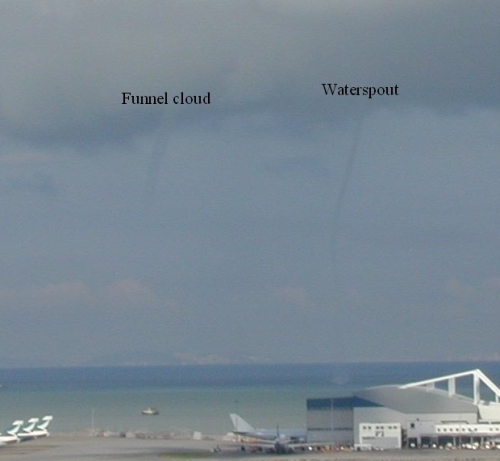

Funnel Cloud
A waterspout is a fast rotating column of air extending from a convective cloud base to the water surface. A rotating column of air that does not touch the water surface is called a funnel cloud.